
Johannes de Vroom, a physician from Breda, as well as by the house behind it on the Houtgracht. In 1682, the house was joined by the neighboring house "Aäron" ( Aaron) with the purchase by Dr. So in 1641 the Franciscans went to the Joodenbuurt, then at the outskirts of the east side of Amsterdam, and opened a house church, the second of its kind in the city, at a house called the "Moyses" (Moses), at the back of the present church. In the first centuries after the Reformation, the public display of Roman Catholic services and accessories was not tolerated – officially forbidden in 1660 – in Amsterdam. Ĭornelis de Vroom, till 1687 (?) pastor in the Mozes- en Aäronkerk In 1970, the present church was designated as a Cultural Heritage Monument ( Dutch: Rijksmonument) of the Netherlands. Originally a clandestine church, it was operated by Franciscan priests at a house on Jodenbreestraat, where the wall tablets of Moses and Aaron hung on the wall. Anthony of Padua ( Dutch: Sint-Anthoniuskerk). Discouraged, Liszt vowed to live a more solitary life, and in 1863 moved to a small, basic apartment in the monastery Madonna del Rosario, just outside of Rome.The Moses and Aaron Church ( Dutch: Mozes en Aäronkerk, pronounced ), in the Waterlooplein neighborhood of Amsterdam, is officially the Roman Catholic Church of St. In that same year, Liszt and Carolyne attempted to wed in Rome, but on the eve of their marriage, their plans were thwarted due to her incomplete divorce papers. In 1860, one of Liszt's rivals, Johannes Brahms, co-published a manifesto against him and the modern composers, just one chapter in what was to become known as the War of the Romantics. In December of 1859, he lost his son Daniel, and in September of 1862, his daughter Blandine also died. The decade that followed was a difficult one for Liszt. For the next 10 years, Liszt's radical and innovative works found their way into the concert halls of Europe, winning him staunch followers and violent adversaries. Liszt's new works inspired eager pupils to seek his guidance. Aesthetically, the symphonic poem is in some ways related to opera it is not sung, but it does unite music and drama. His most famous achievement during this time was the creation of what would become known as the symphonic poem, a type of orchestral musical piece that illustrates or evokes a poem, a story, a painting, or other nonmusical source. The next year, the couple moved to Weimar, Germany, and Liszt began to concentrate on a higher missionóthe creation of new musical forms. Liszt gave his final concert for pay at Elisavetgrad in September, and then spent the winter with the princess at her estate in Woronince. Her influence on him was dramatic she encouraged him to stop touring and, instead, teach and compose, so he could have a more domestic life with her. In 1847, while in Kiev, Liszt met Princess Carolyne zu Sayn-Wittgenstein. His relationship with Marie d'Agoult, which by that point had produced three children, finally ended.
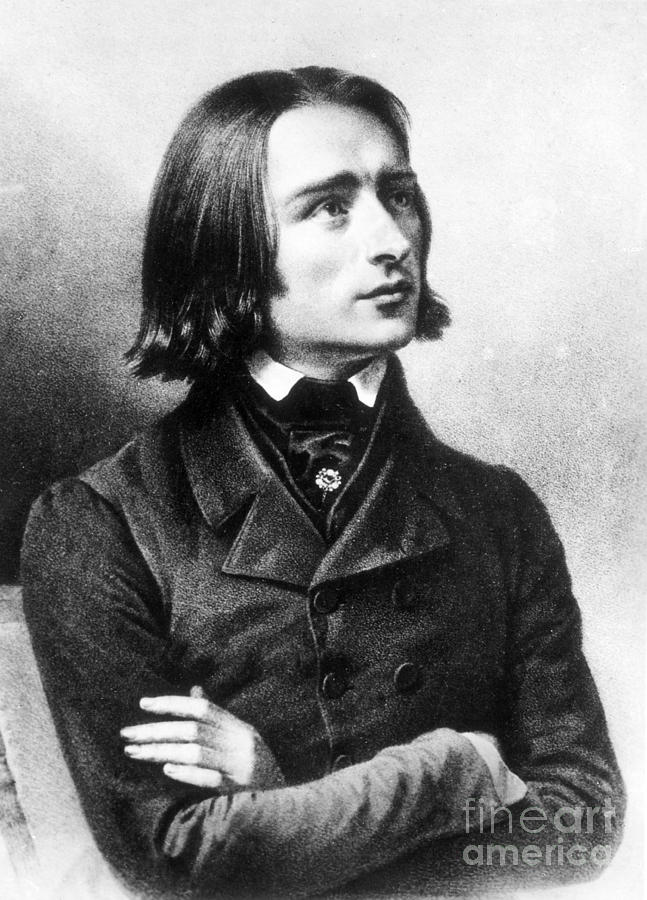

On a personal level, however, matters were less than glorious for Liszt. For example, when in 1842 he found out about the Great Fire of Hamburg, which had destroyed much of the city, he gave concerts to create aid for its thousands of homeless. His reputation was bolstered even further by the fact that he gave away many of his concert proceeds to charities and humanitarian causes. Strengthened by new works and several public performances, Liszt began to take Europe by storm. In 1834, Liszt debuted his piano compositions "Harmonies poétiques et religieuses" and a set of three "Apparitions." Inspired by love and nature, he composed several impressions of the Swiss countryside in "Album d'un voyageur," which would later surface as the "Années de Pèlerinage" ("Years of Pilgrimage").

In 1833, at the age of 22, Liszt met the Comtesse Marie d'Agoult.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
